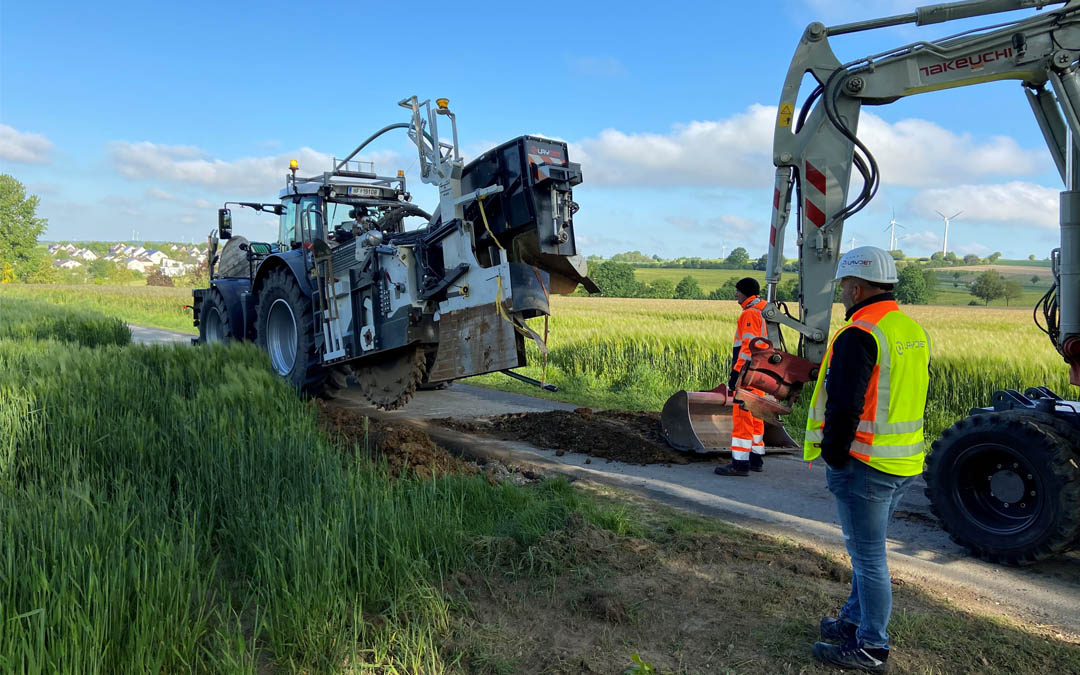
Photo: Kreis Soest / Christoph Hellmann
When implementing broadband projects, different methods are used to lay the fibre optic cables. In contrast to “classic” civil engineering, in which an open trench is dug and the pipes are laid at least one meter deep, alternative laying techniques require less depth – and ideally almost no large excavation pit(s). Modern methods also save time and, not least, money.
In the second part of our “Alternative installation methods” series, you will learn more about trenching. This generic term covers a variety of milling and cutting methods. Usually, trenching is used to lay empty conduits or cables in ground that is covered by a closed surface (e.g. roads or sidewalks).
The trenching method is used in many expansion areas in Germany to ensure rapid and cost-efficient broadband expansion. This alternative laying technique enables shorter construction times, saves costs compared to traditional civil engineering and significantly reduces the disruption to local residents caused by noise, dirt or traffic closures. Only a narrow trench is required to lay empty conduits and fibre optics.
The innovative trenching process is primarily used in footpaths and cycle paths, but is also suitable for road surfaces and unpaved areas as long as they are 60 cm wide and up to 200 cm deep. It can therefore be used both in and out of town.
In contrast to the flush drilling method, trenching involves open civil engineering. With the help of a milling machine, a narrow trench is dug into the ground into which the construction company lays microducts for the fibre optic cables. Shafts for blowing in the fibre optic cables are only necessary every 600 to 800 meters. This process is carried out using compressed air: the fibre optic bundle is more or less shot into the empty tube. The open construction section is then closed again. The final asphalt surface protects the pipes and cables from the weather.

Photos: Deutsche Glasfaser / Martin Wissen
There are various trenching techniques that differ in terms of laying depth and width: nano, micro, mini or macro trenching. Depending on the method and substrate, the laying depth varies between 10 and 80 centimetres. The trench width can vary between 2 and 30 centimetres.
| Nano-trenching | Micro-Trenching | Mini-Trenching | Macro-Trenching | |
| Trench width | up to 2 cm | up to 12 cm | up to 20 cm | up to 30 cm |
| Trench depth | up to 10 cm | up to 30 cm | up to 40 cm | up to 80 cm |
Source: https://www.sicherer-tiefbau.de/positionen/trenching
Nano-trenching: Fast and cost-effective installation directly in the road surface
Nano-trenching has the lowest laying depth and trench width. The narrow slit is made directly in the asphalt using a joint cutter so that microducts can then be inserted. The disadvantage of this variant, which is very easy to implement, is that if the road has to be dug up and/or the road surface renewed in the course of construction work, there is a risk of damaging the fibreglass laid in it.
In contrast, with micro, mini and macro trenching, the slit, which is no wider than an A4 sheet of paper, is cut into the ground – usually at the edge of the road or on the sidewalk – using specially designed cutters. In this way, 250 to 600 meters per day can be processed using the trenching process and fibre optic cables can be blown into the laid microducts.
Layjet: Milling, laying, refilling in a single operation
The relatively new layjet technology is considered to be particularly efficient when it comes to the trenching laying method. The method, invented and now patented by the Austrian company of the same name, has the potential to increase the daily output of pipe laying up to tenfold compared to completely open laying (open trench). Depending on the ground conditions, between 1.5 and 3 kilometers of laid fibre optic cables per day are realistic, the Austrians promise. The Layjet technology is an “all-in-one process”: regardless of the ground conditions, a precisely straight trench is milled next to the road (in the road shoulder) at a depth of 50 to 70 cm. In the same operation, the fibreglass pipe is laid together with a warning tape above it and the trench is backfilled with the material removed and prepared from the ground. Immediately afterwards, a special vehicle compacts the subsoil, which should then be just as stable as before. The advantage of this method is that the road structure remains intact and the fibreglass is laid over any existing cables, which are usually located deeper in the ground. Due to the rapid processing of the construction section, traffic disruption as well as noise and dust pollution are kept to a minimum.
Christoph Hellmann, broadband coordinator for the district of Soest – where the federal government is also supporting broadband expansion with funds from the federal broadband funding programme in conjunction with co-financing from the state of North Rhine-Westphalia – draws a positive conclusion about the laying of fibre optic cables by layjet: “In the municipality of Möhnesee, the new laying method is being used for the first time in the district. It has a great advantage, especially for local residents, because it involves fewer restrictions and is much faster.”
Trenching is one of several cost-saving installation techniques – specific selection depends on individual conditions on site
Overall, trenching is an option in many expansion areas throughout Germany. However, the method is not recommended if the substance of the planned construction section has significant defects, such as large cracks or unevenness. Even if roads cross the installation route or supply lines already exist, other installation methods can be considered depending on the individual situation, such as the flush drilling method or above-ground installation. For long distances and unpaved field and forest paths, the ploughing method is often a more suitable technique. Especially in urban areas and for short construction sections, trenching scores highly as an alternative installation method for laying IT infrastructures thanks to its time-saving, sustainable and cost-efficient expansion.
In the future, the various trenching methods are to be standardised: The German Institute for Standardisation (DIN) wants to turn the laying process into a recognised civil engineering method for which uniform quality standards apply.
Our “Alternative installation methods” series
DIN 18220 comes into effect – Alternative installation methods standardized
DIN 18220 comes into force on July 28. The full name of the standard is "DIN 18220:2023-08. Trenching, milling and ploughing methods for laying empty conduit infrastructures and fiber optic cables for telecommunications networks" and describes in detail the methods...
Classic and alternative installation methods
In order to enable the expansion of fiber optic networks throughout Germany, the players involved have a variety of installation methods at their disposal. The methods must be selected according to topological characteristics and special project requirements. Each...
Robots lay fiber optics in the sewer
An employee prepares the robot for use. Between 100 and 250 meters of fibre optic cable can be laid in this way per day. (Source: Fast Opti-com) Laying fiber optic cables in sewage pipes using robots is one of the alternative installation methods. These offer many...
DIN 18220 comes into effect – Alternative installation methods standardized
DIN 18220 comes into force on July 28. The full name of the standard is "DIN 18220:2023-08. Trenching, milling and ploughing methods for laying empty conduit infrastructures and fiber optic cables for telecommunications networks" and describes in detail the methods...
Classic and alternative installation methods
In order to enable the expansion of fiber optic networks throughout Germany, the players involved have a variety of installation methods at their disposal. The methods must be selected according to topological characteristics and special project requirements. Each...
Robots lay fiber optics in the sewer
An employee prepares the robot for use. Between 100 and 250 meters of fibre optic cable can be laid in this way per day. (Source: Fast Opti-com) Laying fiber optic cables in sewage pipes using robots is one of the alternative installation methods. These offer many...
Using traditional technology for a future-proof broadband connection: the plowing method as an alternative laying technique
The cable plow in use on a field. At the top left is the empty conduit, which is unwound from the drum and then laid in the freshly plowed furrow Photo: IBZ Neubauer When implementing broadband projects, different methods are used to lay the fiber optic cables. In...