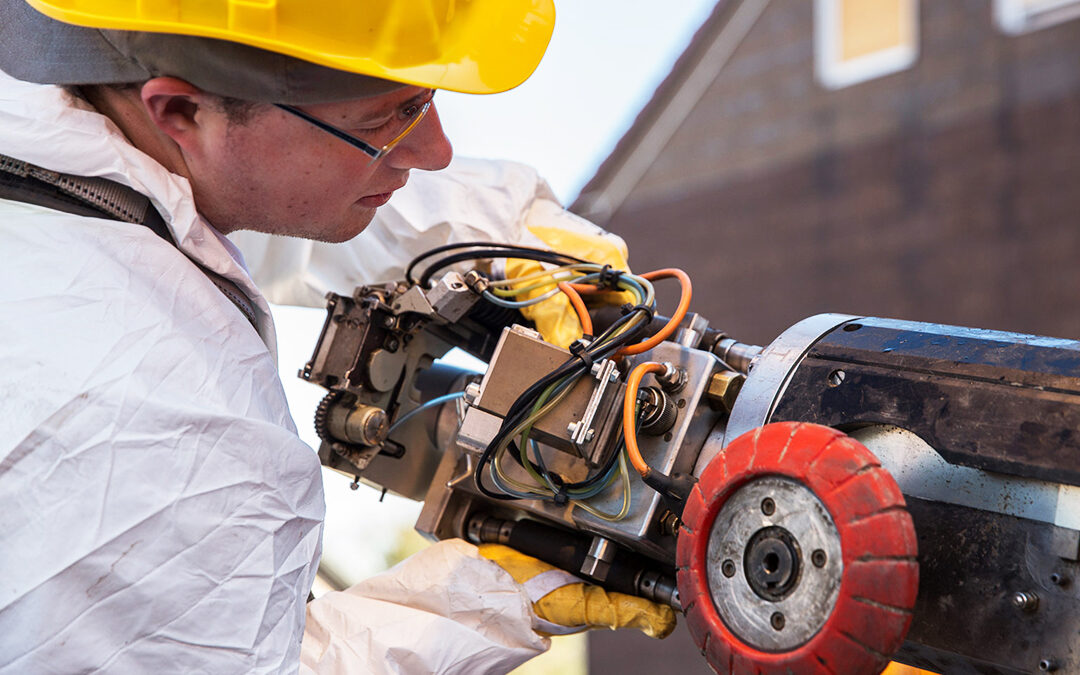
(Source: Fast Opti-com)
Laying fiber optic cables in sewage pipes using robots is one of the alternative installation methods. These offer many advantages, such as the fact that they are relatively easy to approve and there are few surprises during installation.
The idea is obvious. Instead of building new routes, an existing infrastructure – the wastewater network – is simply used. Civil engineering work and the associated disruption to traffic flow, damage to road surfaces and interference with the environment are therefore avoided as far as possible. With a laying capacity of between 100 and 250 meters per day, the method is competitive. Using conventional civil engineering technology, around 100 meters of fibre optic cable can be laid per day. However, the costs for the extension in the sewer are significantly lower than with conventional laying methods (just under 50 euros compared to 100 euros average price per meter). In addition, construction site costs are reduced and no complete road closures are necessary. A small, secure working area is all that is needed to insert the robot. Among other things, the environment is protected as there is no damage to the roots of trees. Possible contaminated sites in the ground also have no impact on the costs. In the sewer, the network is additionally protected by the thickness of the walls used for the sewer system, and only permission for the use of the sewer must be obtained in advance, which requires agreements and contracts with the operator.
There are basically two different methods: In the first variant, empty pipes are laid. The alternative is to insert an inliner into the sewer. The advantage of the first option is that the pipes can be replaced very easily at a later date, while the latter option is more suitable for renovating sewers. The glass fiber is laid either by laying robots or manually. In the case of accessible sewers, a person can of course do the work. Laying can be carried out using tension rings, anchors or hose and short liners. The empty conduits are attached to the inner wall of the pipes and robots can be used in smaller pipes. Of course, the technical suitability and condition of the wastewater systems must be checked in advance.
Practical examples Staßfurt and Bornheim
The method is tried and tested and has been in use for many years. Positive experience with the technology was gained in a project in the Salzland district in Saxony-Anhalt. In Staßfurt, a busy regional railway line had to be crossed underneath. Using this installation method, the fiber optic cables could be laid in the existing sewers. An empty fiber optic conduit system was installed, which makes it possible to replace cable strands at any time. Branching and connection points were installed in the shafts connecting the sewer system. The robot then fixed the retaining clips to the wall of the duct. A 15.5 millimetre thick and corrugated empty conduit made of stainless steel was clamped into these clips, which permanently and reliably protects the fiber optic cable running through it from moisture, animal bites and other damage. Another successful example of laying fiber optic cables in sewers is the broadband expansion in Bornheim. Here, around 45 km of fiber optic cable was laid underground through the existing sewers.
Our “Alternative installation methods” series
DIN 18220 comes into effect – Alternative installation methods standardized
DIN 18220 comes into force on July 28. The full name of the standard is "DIN 18220:2023-08. Trenching, milling and ploughing methods for laying empty conduit infrastructures and fiber optic cables for telecommunications networks" and describes in detail the methods...
Classic and alternative installation methods
In order to enable the expansion of fiber optic networks throughout Germany, the players involved have a variety of installation methods at their disposal. The methods must be selected according to topological characteristics and special project requirements. Each...
Using traditional technology for a future-proof broadband connection: the plowing method as an alternative laying technique
The cable plow in use on a field. At the top left is the empty conduit, which is unwound from the drum and then laid in the freshly plowed furrow Photo: IBZ Neubauer When implementing broadband projects, different methods are used to lay the fiber optic cables. In...
Above-Ground Fibre Optic Installation – a Fast and Cost-Effective Alternative to Traditional Underground Construction
Photo: Adobe Stock When implementing broadband projects, different methods are used to lay the fibre optic cables. In contrast to "classic" civil engineering, in which an open trench is dug and the pipes are laid at least one meter deep, alternative laying techniques...
DIN 18220 comes into effect – Alternative installation methods standardized
DIN 18220 comes into force on July 28. The full name of the standard is "DIN 18220:2023-08. Trenching, milling and ploughing methods for laying empty conduit infrastructures and fiber optic cables for telecommunications networks" and describes in detail the methods...
Classic and alternative installation methods
In order to enable the expansion of fiber optic networks throughout Germany, the players involved have a variety of installation methods at their disposal. The methods must be selected according to topological characteristics and special project requirements. Each...
Using traditional technology for a future-proof broadband connection: the plowing method as an alternative laying technique
The cable plow in use on a field. At the top left is the empty conduit, which is unwound from the drum and then laid in the freshly plowed furrow Photo: IBZ Neubauer When implementing broadband projects, different methods are used to lay the fiber optic cables. In...
Above-Ground Fibre Optic Installation – a Fast and Cost-Effective Alternative to Traditional Underground Construction
Photo: Adobe Stock When implementing broadband projects, different methods are used to lay the fibre optic cables. In contrast to "classic" civil engineering, in which an open trench is dug and the pipes are laid at least one meter deep, alternative laying techniques...